Paper Session NATURE(S)
TACK Conference Proceedings
BODY OF KNOWLEDGE : KNOWING BODIES
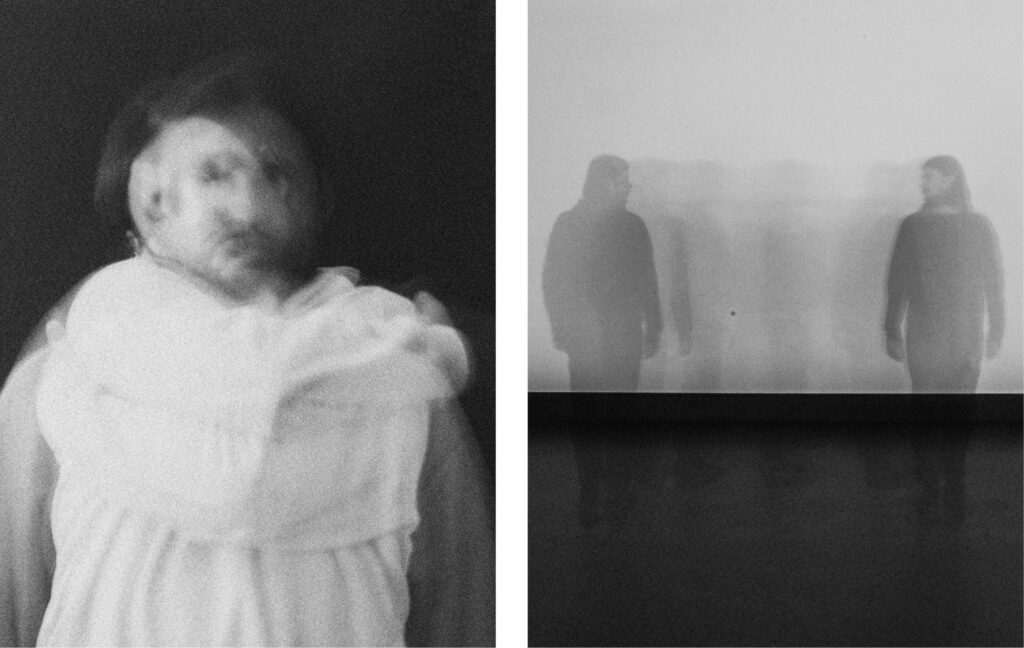
Fig. 1.
Sofia Pintzou, contribution to »Sasha Waltz & Guests’ Tanztagebuch«, 2020, interpreting choreographic material from Sasha Waltz’ »noBody«, first performed 2002 at Schaubühne am Lehniner Platz in Berlin, film stills from the video, online: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=bj-dVgonIT0, accessed July 25, 2023.
ABSTRACT
This contribution addresses tacit knowledge as an embodied form of knowing and traces the potential of the body to inform and explore, contain and convey, obtain and express architectural knowledge — in the experiencing, designing, creating, and living of architectural space. If, as framed by Polanyi, »we know more than we can tell«, focusing on the body and its immanent knowledge allows to access immediate forms of architectural knowledge. Experience, memory, and the capacity for anticipation are equally rooted in the body; corporeally anchored, contained in, and inscribed to the body. Respectively, creative imagination in architectural design relies upon the body. Through knowing how we experience architecture, we are eager to anticipate future perception in architectural design.
Following my doctoral thesis, entitled “Impulses and Dialogues of Architecture and the Body”, I present the knowledge of the body as a contribution to the body of knowledge of architecture: Using the example of the working method and oeuvre of Sasha Waltz & Guests – which I investigate against the background of my own artistic practice, especially in in-situ and site-specific performances, as well as my attempts at the including of somatic practices into my academic teaching in the field of architecture – I exploit the body as a medium of spatial research, and as an immediate form of conveyance and expression in the discipline of architecture.
Katharina Voigt