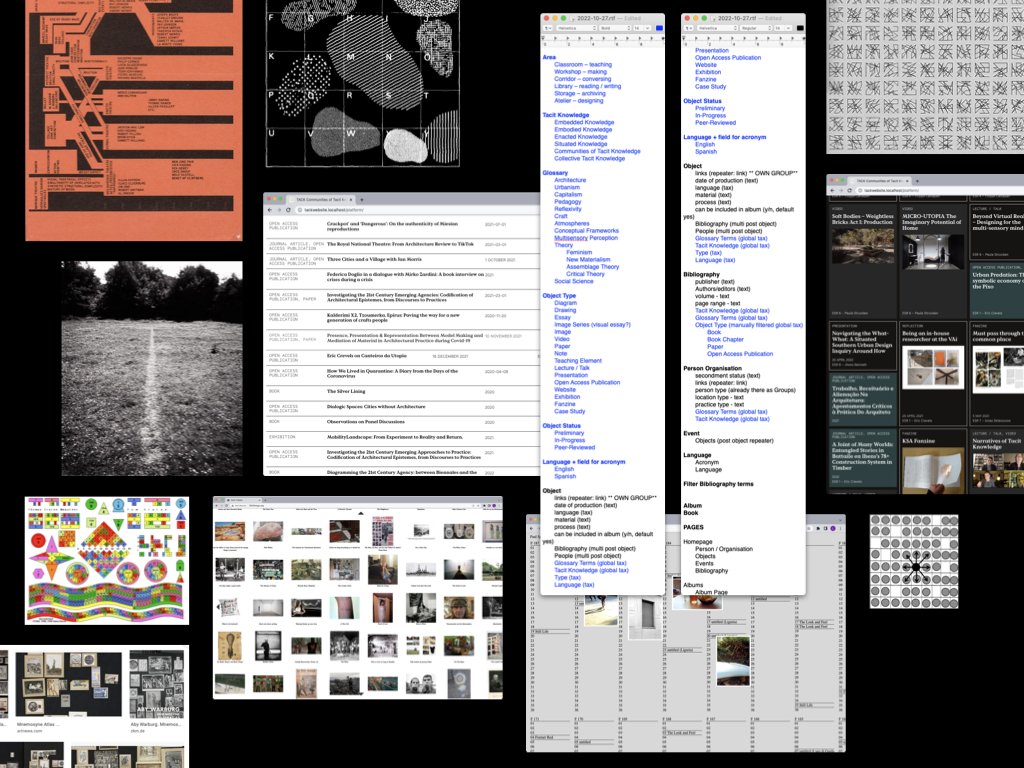
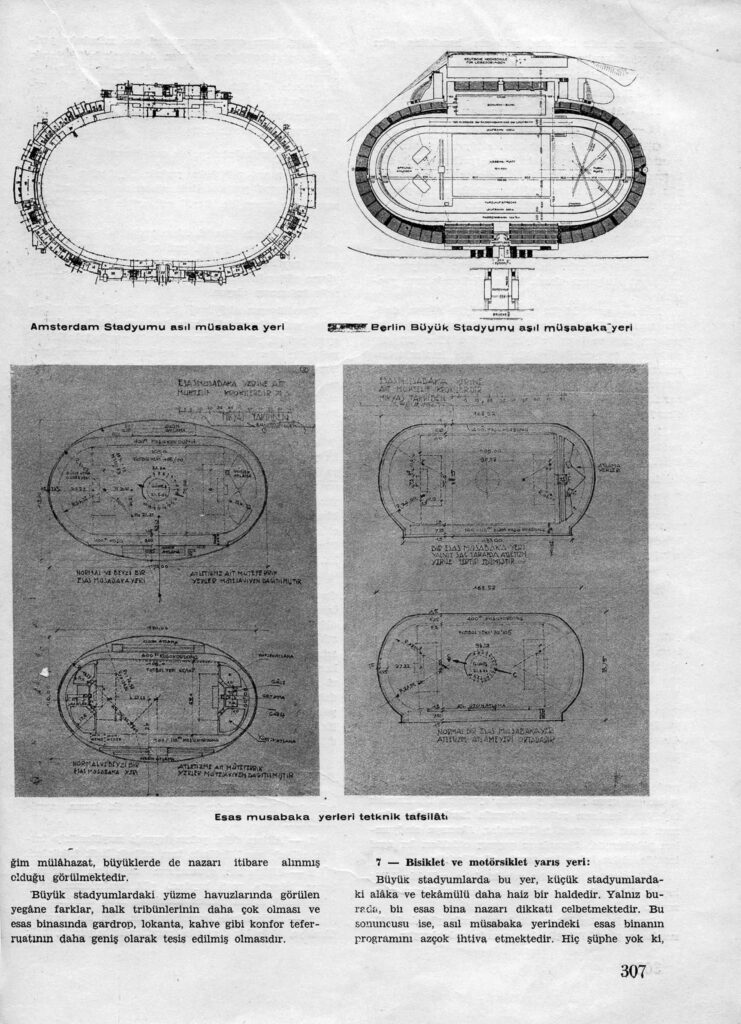
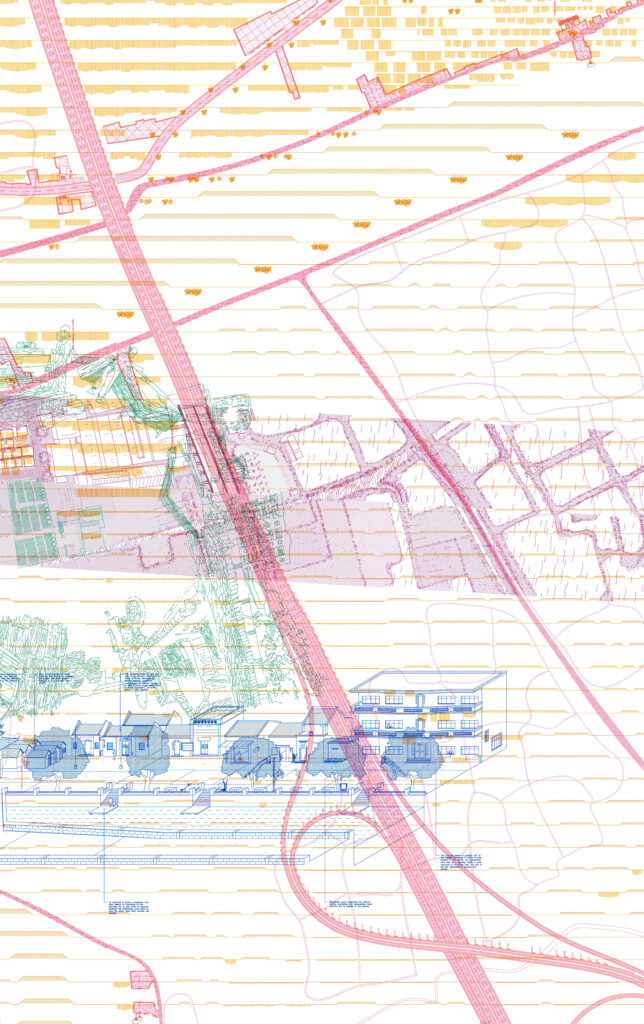
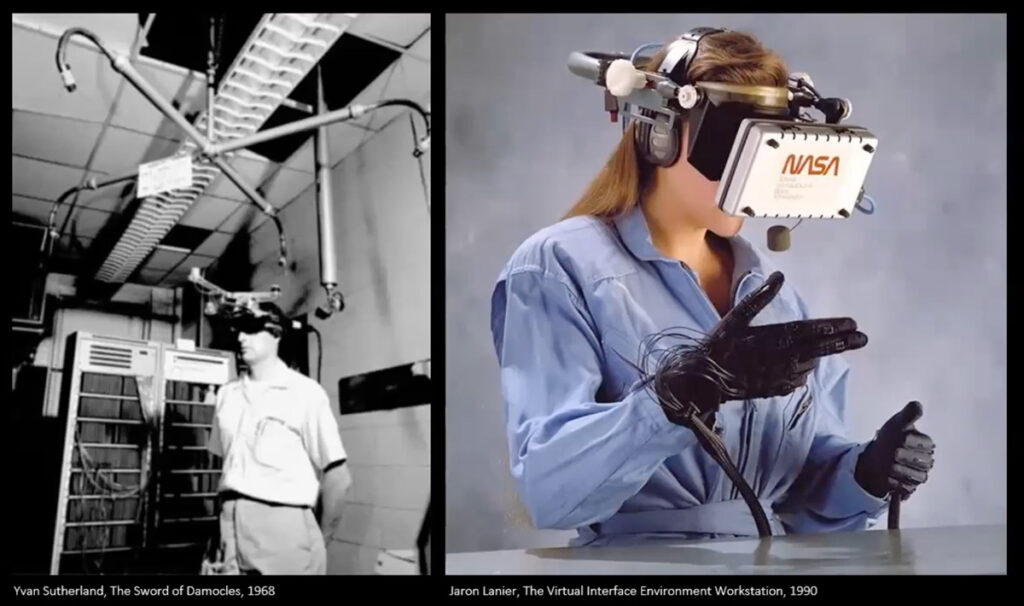
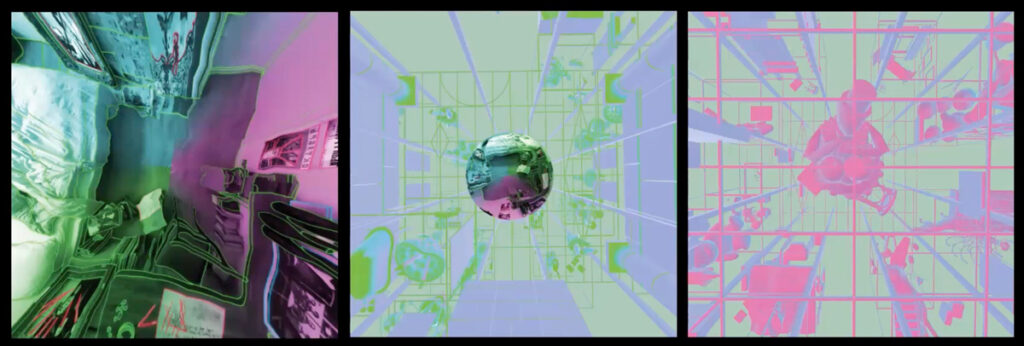
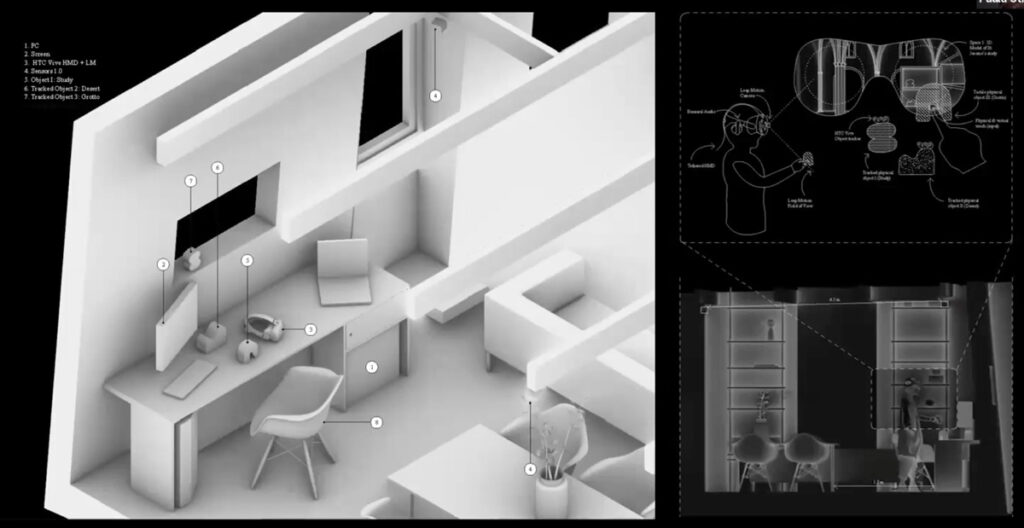
Diagram
Fanzine
Interview
Interview with Kristina Schinegger and Stefan Rutzinger

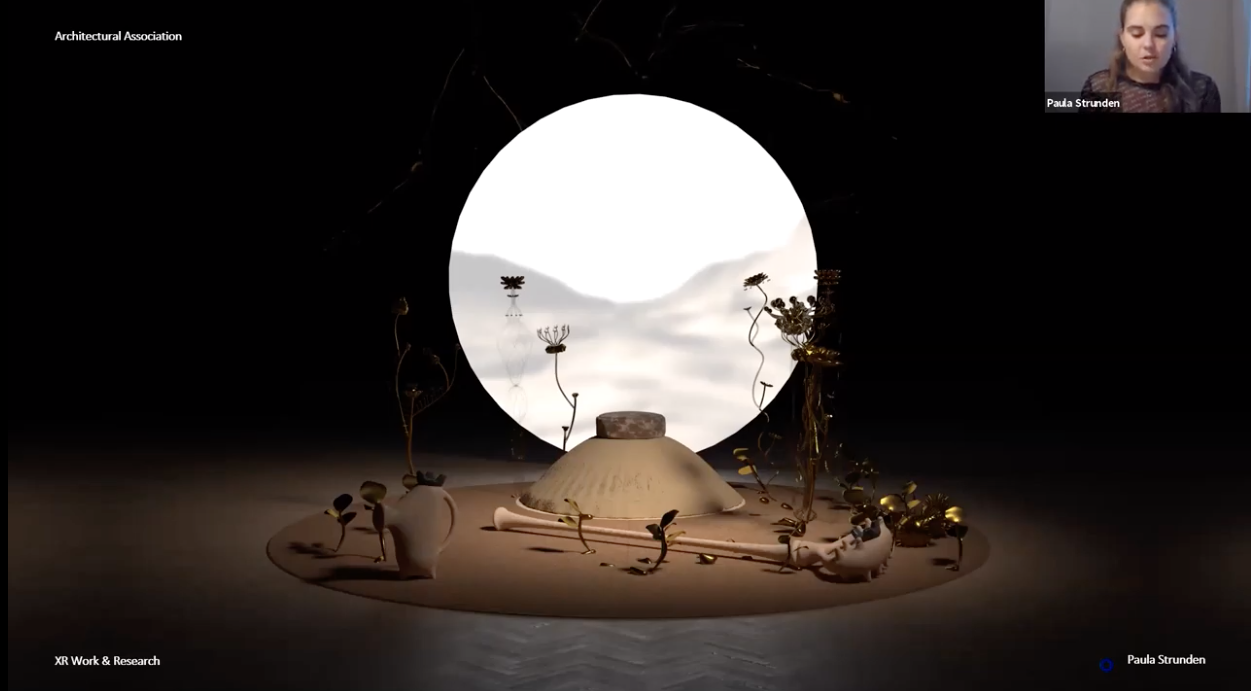
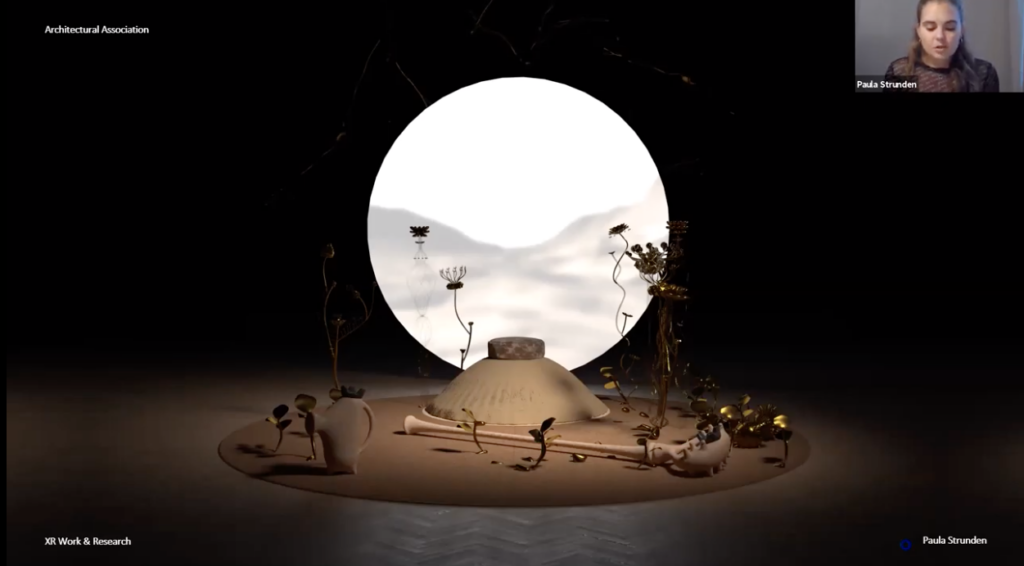
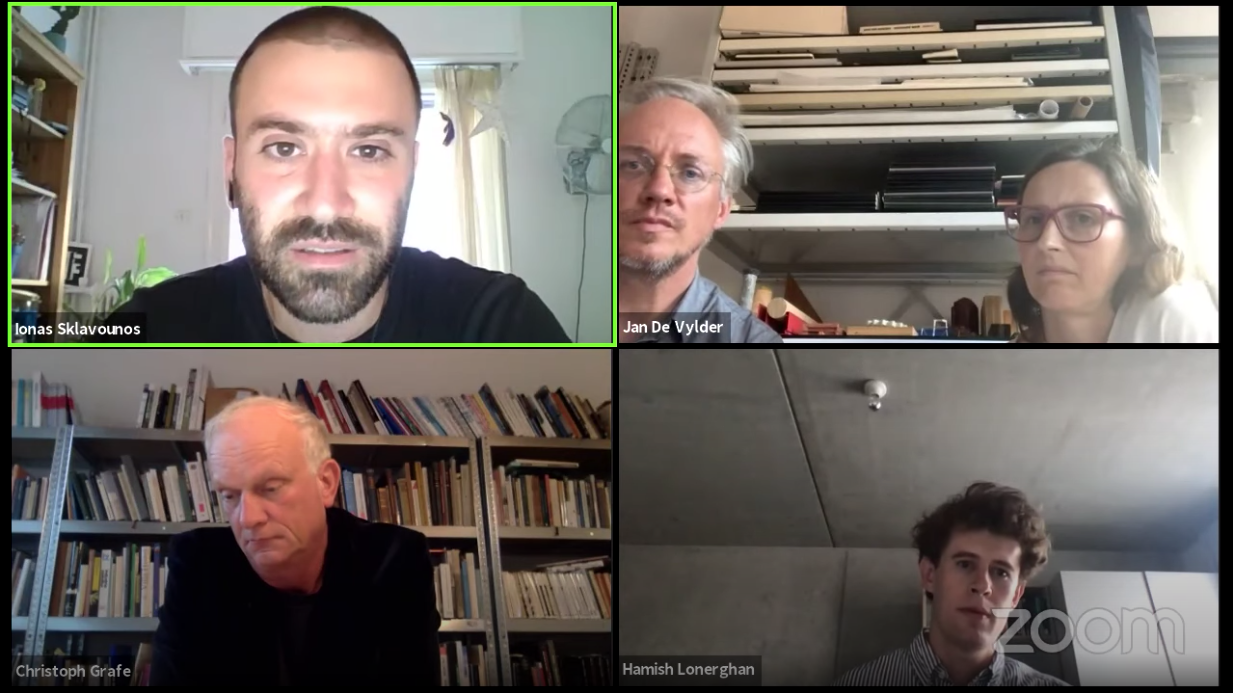
On 7 April 2021, Kristina Schinegger (KS) and Stefan Rutzinger (SR) were interviewed on Zoom by Paula Strunden, PhD Candidate, Academy of Fine Arts Vienna.
Paula Strunden
SOMA Architecture
Diagram
Fanzine
Interview
April 7, 2021
View
Interview with Kristina Schinegger and Stefan Rutzinger
Paula Strunden
SOMA Architecture


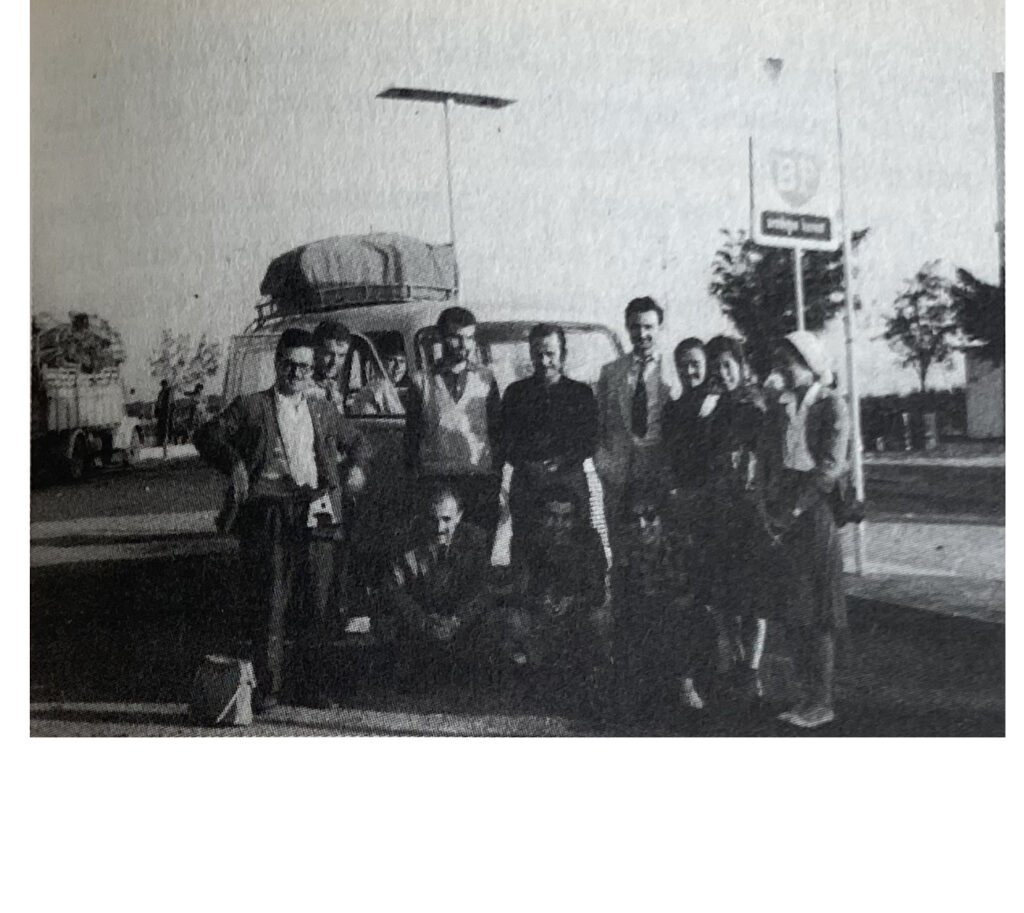
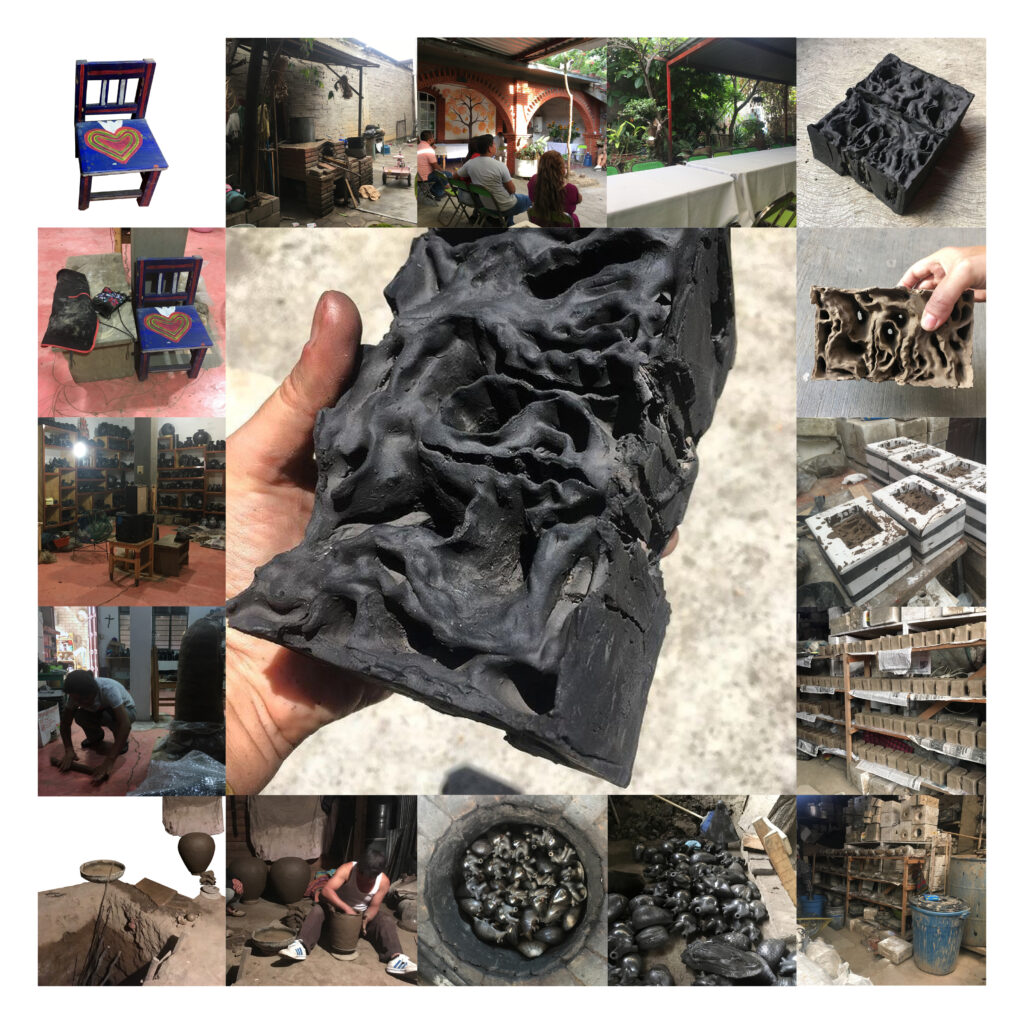
© Paula Strunden

© Paula Strunden

© Paula Strunden

© Paula Strunden

© Paula Strunden

© Paula Strunden
On 7 April 2021, Kristina Schinegger (KS) and Stefan Rutzinger (SR) were interviewed on Zoom by Paula Strunden, PhD Candidate, Academy of Fine Arts Vienna.