ABSTRACT
Tacit knowledge in architectural education is slippery. It encompasses a broad range of unconscious, embodied, social and otherwise hidden forms of knowing. On one hand, this means that it manifests in different ways depending on the pedagogical format or context. On the other, it resists explanation through the traditional, and largely explicit, tools of academic writing. Therefore, rather than seeking to define it, this paper proposes three approaches for locating and describing it. First, forms of tacit knowing—which we rely on, often without thinking, in our studio, school, or regional culture—become more visible in “moments of encounter” between communities. Second, discussions and negotiations of tacit knowledge often occur through architectural materials: drawings, models, texts, buildings. Third, “moments of tacit encounter” require more evocative and speculative methods of writing and representation, with different evidentiary standards. To test these approaches, this paper narrates two “moments of encounter” as case studies, encompassing different pedagogical formats, actors, writing methods, and revealing different forms of tacit knowledge.
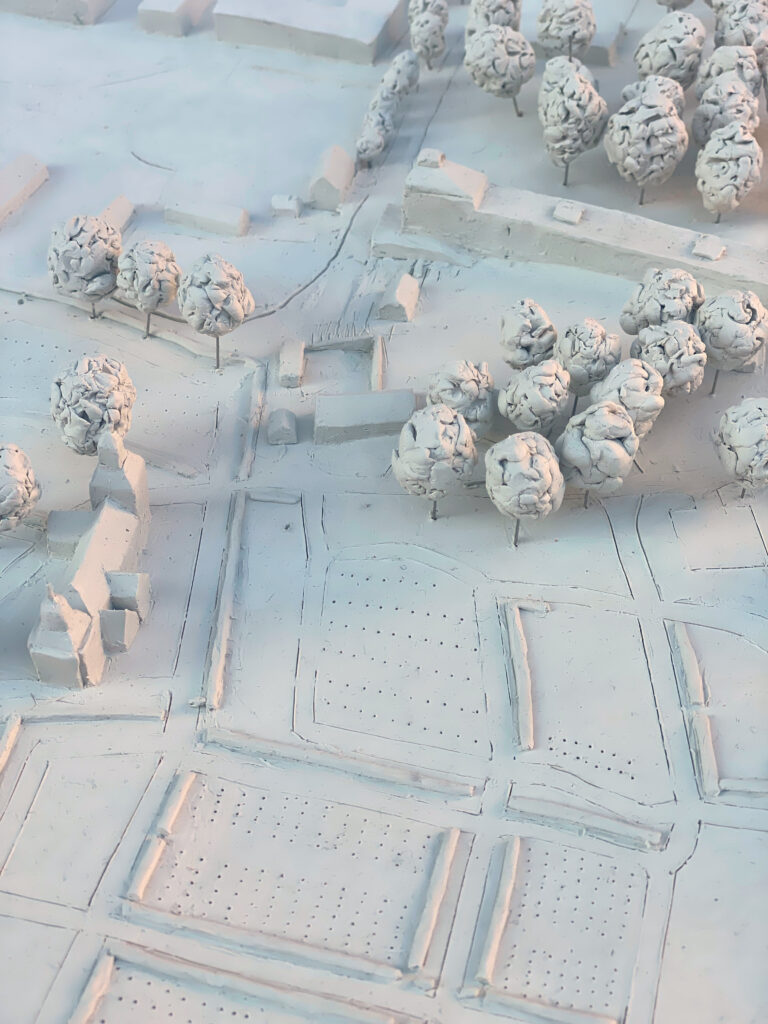
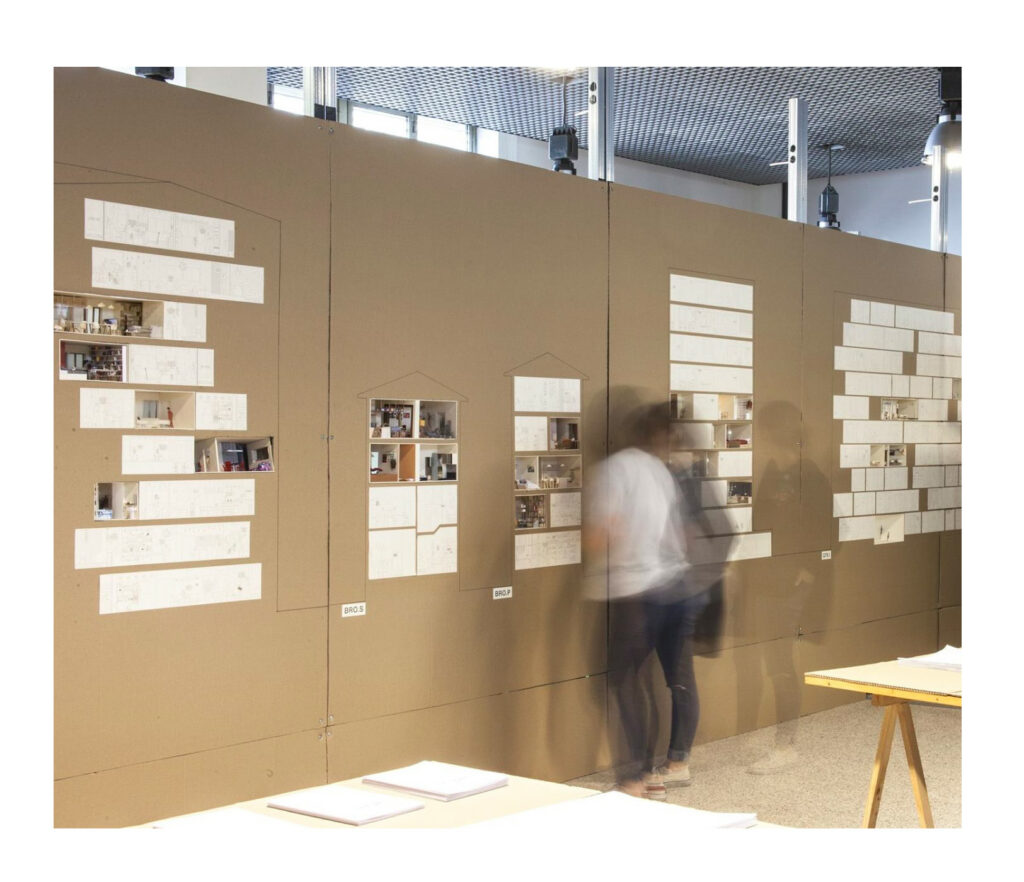
In 2020, I arrived at ETH Zurich, where I began an autoethnographic study of tacit knowledge in discussions between critics across design studios. I was drawn to the realistic models of Studio Caruso, which I first encountered in my architectural studies in Australia. There, they represented a hitherto unimaginable departure from model abstraction. In Zurich, though, some critics were less dazzled, questioning the labor they required. Elsewhere, realistic models had been at the center of right-wing outrage over a kiosk designed by Caruso’s office in Escher-Wyss Platz in 2007. Around these models, the tacit architectural expectations of various groups seemed to reveal itself.
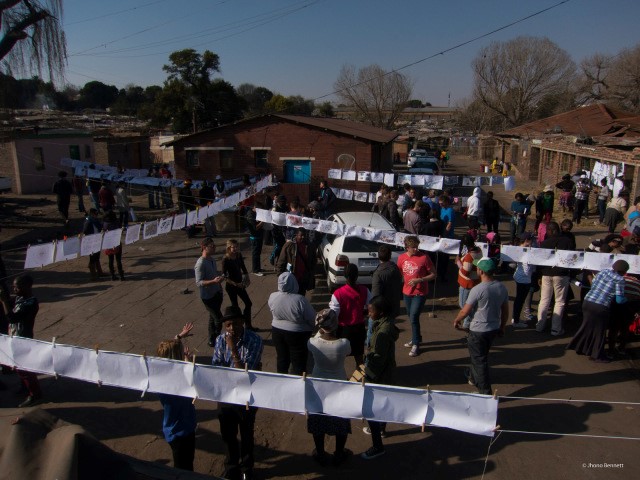
In 2021, I organized a summer school in Rotterdam on summer schools. Over five days, we re-enacted a charette exercise originally set for the 1986 edition of the International Laboratory of Architecture and Urban Design (ILAUD): the summer workshops founded by Giancarlo de Carlo in Urbino. Summer schools are ephemeral in nature—intense, productive, social, life-changing, but only for a few weeks—leaving little evidence of their tacit dimension for us to study today. Re-enacting it ourselves, coming from different educational backgrounds, we started to understand something of what it must have felt like in 1986. We experienced the clashes and arguments, and overcome them through drawings or by discussing images, by talking in those informal moments on the staircase or over lunch.