ABSTRACT
In the manifold spectrum of how tacit knowledge can be conceived in architecture, the contribution aims to investigate that embedded in the architects' design process by reflecting on the codes they employ.
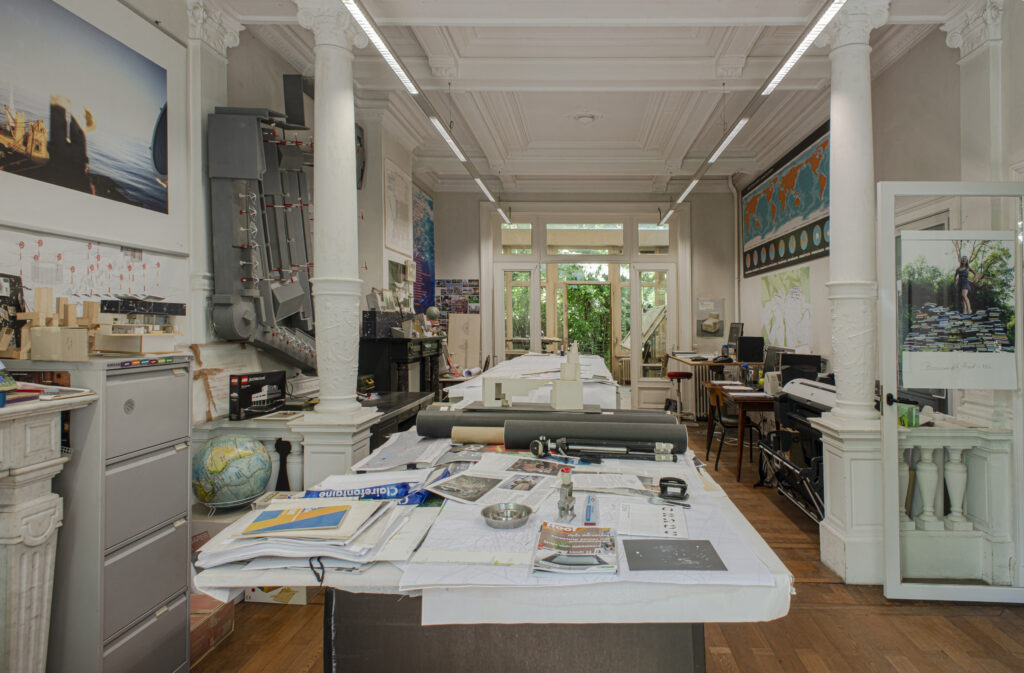
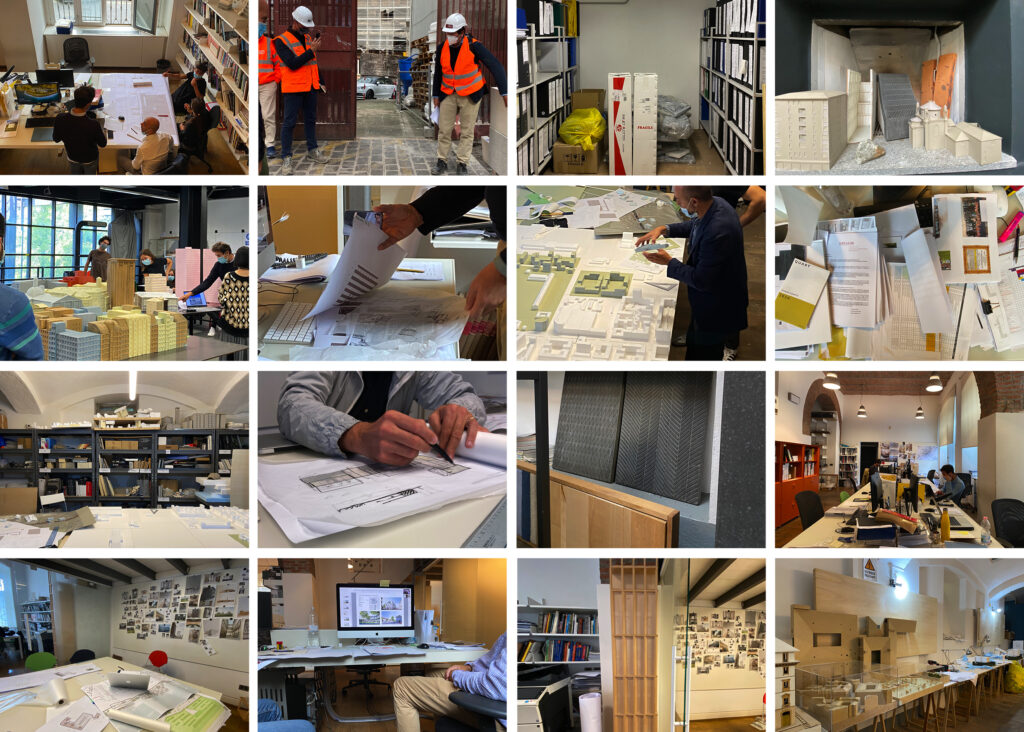
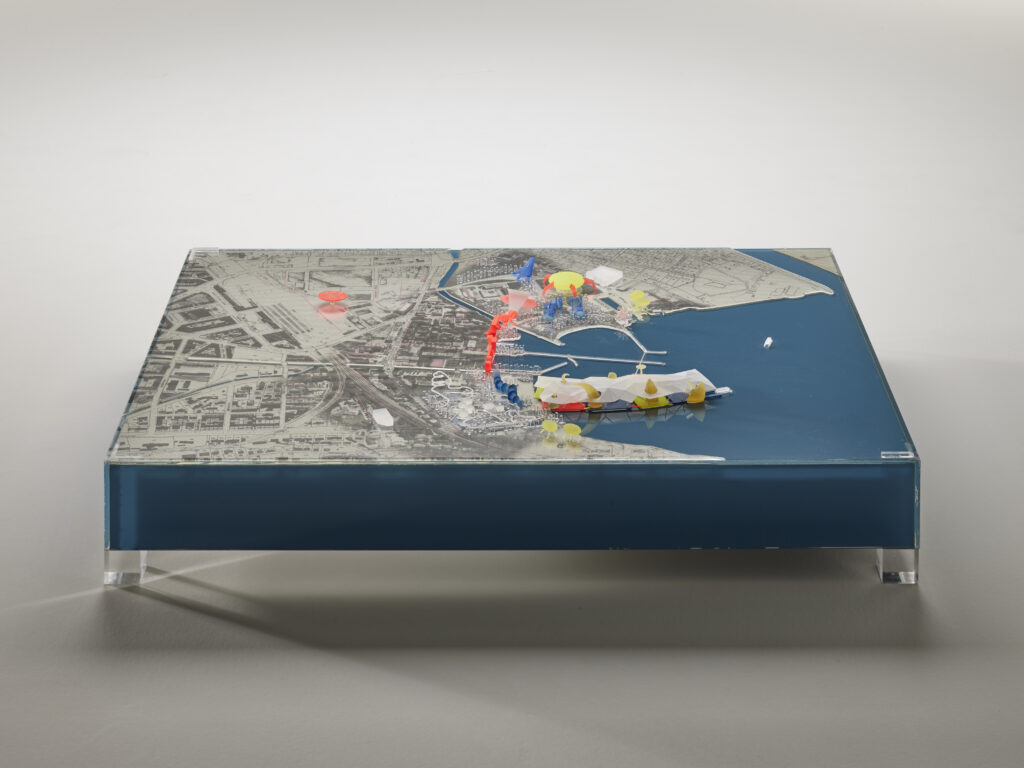
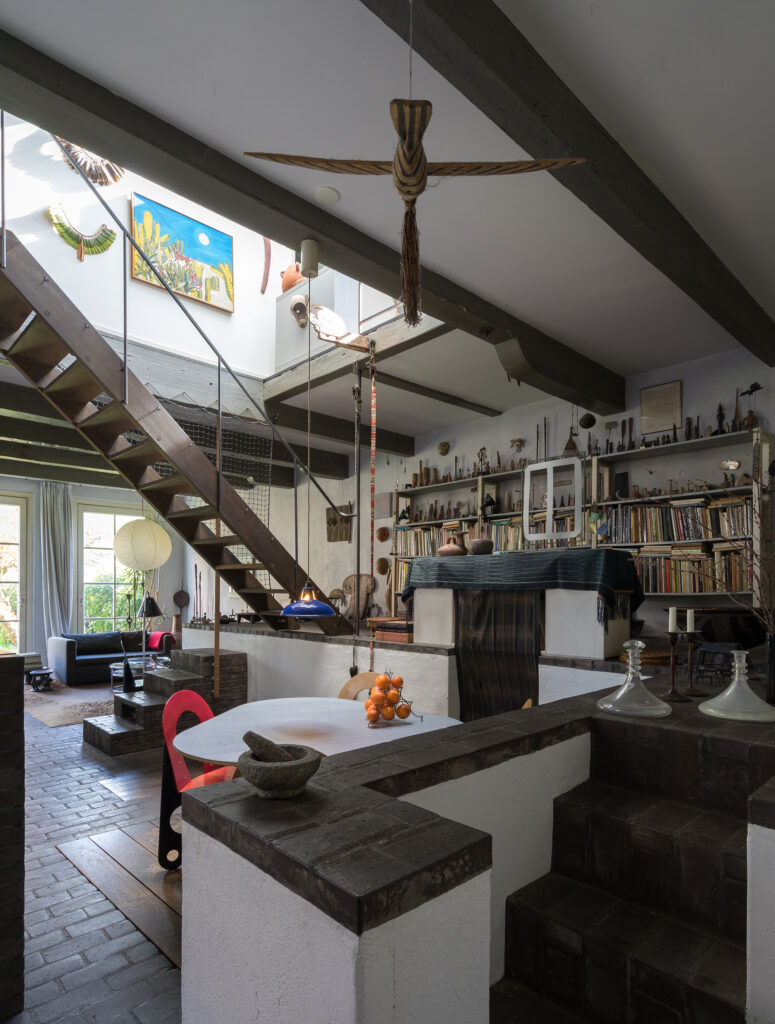
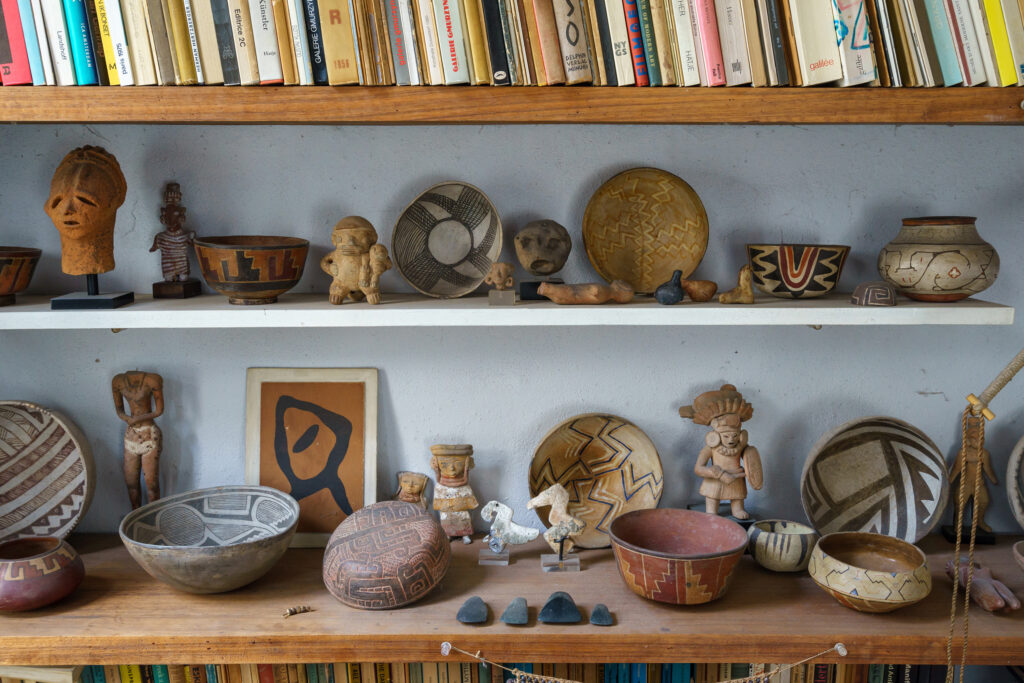
If the vectors are tools or communicative materials –i.e., drawings, sketches, models, texts, etc.– used for transmission, the codes are here interpreted as those characters –whether in the form of recurring patterns or aesthetic choices, technical solutions, vocabulary, etc.– that define the specificity of a practice. As the DNA of an office, and not just of its principal, as Rem Koolhaas argues (Winston, 2016), they articulate across different levels depending on the context within which they are shared: spanning from the ones used within the practice itself –forming the basis for collaboration between different project team members;– to those adopted externally to communicate with both clients and an extended community of practice.
Differences in terms of codes might parallel diverse methods for their investigation. Indeed, for the former, the use of an ethnographic approach capable of unpacking specificities from within seems to be the most adequate –i.e., revealing how the implicit values of a practice are transferred into form through a collective process mediated by multiple actors;– for the latter, instead, it would be more proper to employ public occasions as a pretext through which to decipher a shared “language.” (Eco, 1976).
In general, the paper argues that codification processes are necessarily conditioned by the context in which they take place, by the positioning within the disciplinary debate, and by the actors (Latour and Yaneva. 2008) participating in their development. These closely interrelated aspects constitute the tacit knowledge inherent to a practice. Hence, although capable of changing over time, such knowledge is a unique and characterized product for an office. At the same time, it is the contribution that each firm provides in shaping its community of practice, whose shared knowledge unfolds through exchanges and encounters.